How it works > the natural algae click control functionality
The algae free device is comparable to a Hi-Fi stereo system that generates high-precision acoustic click signals. These click signals are sent to the underwater piezo speaker, the click generator. From the click generator, high-precision click tones are sent as a complex sound wave pattern horizontally under the water surface.
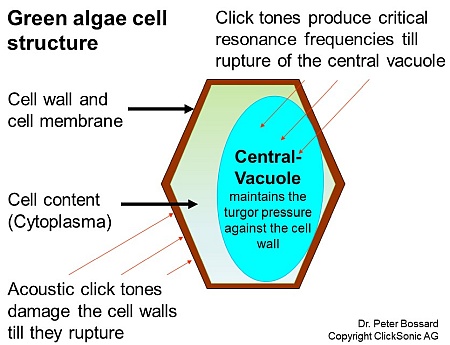
Due to the solar exposure, nutrients and warm temperatures, the most active photosynthesis, algae production, takes place in the upper water layer. In this layer the main signal of the click tones is sent, preventing algae from growing further. The resonance vibrations damage the cell walls and hollow bodies of the algae cell and the cell contents escape. The cell walls of the empty algae sink to the ground and are broken down by the present bacteria.
The permanent use of the effective clicks prevents new algae from forming while existing algae die off. All native algae species in natural waters can thus be treated in an environment-friendly manner: Floating algae within 1 week, green algae, blue-green algae within 3-4 weeks and tough thread algae in up to 8 weeks.
Ultrasound can be produced with different intensities that can have varying effects on biological cells.
High power ultrasound creates cavitation of micro bubbles forming around the the ultrasonic output device (transducer) by producing very high intensities. The very quick collapse of bubbles in water triggered by the ultrasound is called acoustic cavitation. This ends in fast cell death as a result of the high temperatures (>5000K) and pressures (>MPa). Power ultrasound frequency in the 20 - 100 kHz range is used mainly in sonochemistry.
Low power ultrasound produces no cavitation effect. Similar to the clicks of sperm whales, the ultrasound acoustic system produces specific ultrasonic sound tones. These tones produce critical resonance frequencies on its own natural frequency of cell membranes, such as algae gas vesicles, vacuoles, plasmalemma cells. These clicks cause disruption of the algae cell membranes, which results in them breaking or tearing. Depending on the algae species, the rupture can take up to several days or months. The algae are brought to their life end by loss of critical life functions, such as plasmalemma. In ponds and lakes, low power frequency in the 20 - 200 kHz range are used.

Healthy Cladophora from the field trial near Lucerne, Switzerland.

After 4 weeks of exposure to the algae removal device, the first damage to the chloroplasts and cell walls can already be seen under the microscope.

After 8 weeks of application, the vital cell contents have leaked and the algae are no longer viable.
Blue-green algae (cyanobacteria), smear algae were the first inhabitants on earth, since more than 3.5 billion years. Blue algae are bacteria and coat the water in a blue-green colour, hence the name blue algae.
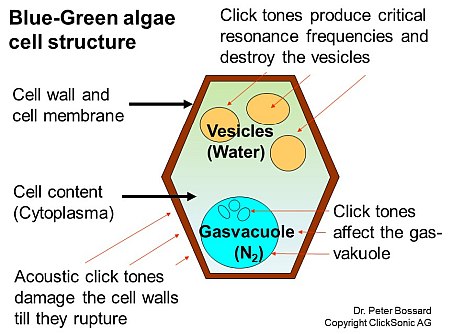
All types of algae that can be found in our natural waters are kept in check by the click tones generated: Prokaryotes, organisms without cell nucleus, such as e.g. blue algae (cyanobacteria) or as smear algae, as well as eukaryotes or eukaryontes, organisms with cell nucleus and cell membrane, about 10-100 times larger than prokaryotes, such as Chlorophyta (green algae), filamentous algae (wire algae), diatoms (Bacillariophyta), golden brown algae (Chrysophyceae), Phaeophyta (brown algae), Pyrrhophyta or Dinophyta (dinoflagellates), Rhodophyta (red algae).
Other living habitants in the water are not affected by the click sounds, neither flora nor fauna. Similar sounds occur in nature, for example when water hits a pond surface. The algae stick to the biofilm of a slime layer where microorganisms are embedded. They consist mainly of bacteria, fungi and protozoa (pathogens). The microorganisms colonise all water surfaces and form communities. The visible biofilm is reduced by approx. 2/3 thirds due to the elimination of algae.
Amphibians: frogs, newts, toads and freshwater fish only hear very low sounds between 50 and 600 Hertz. All sounds above 1000 Hertz are not heard by freshwater fish. Similar clicking sounds are produced by dolphins and whales and are used for communication, orientation and echolocation. These natural ultra sound click sounds are very similar to the clicks generated by algae clearance devices.
Case Studies

Documented case studies for semi-natural water objects:
• Fountain pond with boulder
• Swimming pond
• Event show pond
• Swimming lake
Scientific Studies

Recent scientific redearch studies in low-frequency, low-power ultrasonic waves confirm the effects to algae and bacteria.
References of ultrasonic frequency and power on algae suspensions, etc.