Combating algae in the pond - tips that help!
Is your pond already turbid in spring and full of algae in summer?

Anyone who knows a garden pond knows the problem: algae. Especially in spring, when the pond or pool is being restored to its former glory, algae are the ones to fight. It is not always necessary to replace the entire water, because there are basically other ways and means of preventing algae growth and effectively combating the algae.
- Algae in the pond, algae explosion: How are they actually formed?
- How does it come to an increasing nutrient content in water?
- Algae in the pool: How can algae formation be prevented?
- More algae in the pond " break the vicious circle
- Do plants help against algae in garden ponds?
- Which algae are particularly annoying?
- Fight green algae in the pond
- Fight floating algae in the pond
- How can I fight thread algae?
- How toxic are blue-green algae Tychonema, cyanobacteria?
- Brown algae in the pond are mostly diatoms
Algae explosion in the pond: How are they actually formed?
In fact every pond has them: Algae of all kinds. Ideally, the quantity of algae present is manageable. They usually become annoying when the nutrient content of the water increases significantly and the pond water becomes turbid. This is because the increasing nutrient content, which is primarily measured by phosphate and nitrate content, drastically improves the "living conditions" of algae. If rising temperatures and direct sunlight are added to this, there is actually nothing to stop algae growth. For the algae to grow, they need:
- Light - Strong sunlight favours algae growth
- Carbon dioxide CO2 - Chemical compound of carbon and oxygen as a colourless gas
- Wasser - Nährstoffe aus dem Wasser, z.B. Nitrate und Phosphate

When there is a lot of sunshine, the algae, especially green algae and filamentous algae, rise to the water surface due to the gases which are formed. The algae explosion is in full swing and an appalling picture is created, the dense biofilm also closes the water surface. The algae carpet is only broken through during heavy rain or by manual pond cleaning.
How does it actually come to an increasing nutrient supply in water?
In principle, it is quite simple: in ponds with fish stocking, the most common sources of phosphate are, for example, fish excrement and an excess supply of feed. Both sink to the bottom, where they are gradually broken down into their constituents. A further reason for a sharp increase in nutrients is a wide range of weather conditions. Wind and storms in autumn carry leaves and other things into the water. Rain also washes substances into the pond that have a negative influence on the water quality. For example, nutrient-rich garden soil or fertilizers of all kinds.
Algae in the pool: How can green algae formation be prevented?

No algae in the natural pool thanks to a correctly designed filter zone. Here the balance is right, the nutrients are absorbed and the pond remains stable (algae free).
The most important thing is to extract the nutrients from the pond water.
The nutrients in the pond are removed by regularly shearing and fishing the algae. Most of the nutrients are also removed from the water during pond maintenance. The pond is renovated by removing the layer of mud, decaying plants, foliage, dust and fish droppings. At the same time, old pond soil should be replaced by new, nutrient-poor substrate.
Pool owners have an advantage over pond owners in that they have access to chlorine, which generally counteracts algae growth. It is important to ensure that the chlorine content of the water is always within the correct range. The ideal value is between 1.0 and 3.0. A value below 1.0 is suboptimal - in these cases the chlorine content should be increased by appropriate means.
In addition to the chlorine content, it is important that the pool filter is cleaned regularly. This will prevent the nutrient content of the water from increasing. The same applies to external contamination: Leaves, branches and other things from the garden have no place in the pool. To protect the pool from falling leaves in the autumn, a net or cover is a suitable solution.
Not only pool users enjoy the direct sunlight, but also algae. In general, algae spread faster if they have an intensive light source. It is understandable that pool owners are reluctant to give up sunlight and set up the pool in the shade. However, when the pool is not in use, it should be covered with a tarpaulin or other cover to prevent sunlight from entering the pool.
More algae in the pond » break the vicious circle
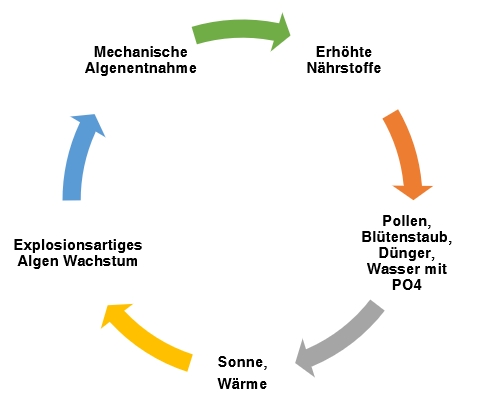
Algae growth starts already in spring due to the increased nutrient occurrence in the pond caused by the pollen. Algae in the pond, breaking the vicious circle. The explosive algae growth increases in summer due to the sunlight and the warming of the water. Supported by phosphates from agricultural fertilizers contained in the groundwater and tap water or by infiltrating lawn fertilizer, inputs from fish food, water birds, possibly arbour input from nearby trees.
The algae concentrate and store the nutrients from the water and it is necessary to break this vicious circle before the dying algae material sinks to the ground and bunkers digested sludge for the next year.
By mechanically removing the algae by hand with the leaf rake, the bundled nutrient packages are extracted from the pond. This process is all the more important with the use of the G-Sonic algae free devices. When the cell walls are destroyed, the cell structure becomes loose and the size of the cells increases many times over. The bound nutrients return to the water and provide food for the new algae growth.
Tip: Preventive measures for clear water
Do plants help against algae in garden ponds?
Aquatic plants also need phosphate, nitrate and other nutrients to grow. The more plants in the pond, the faster the nutrients are absorbed and thus bound by the plant growth.
Planting tips for the pond system: If you cut back the aquatic plants vigorously from time to time, the nutrients will be removed from the nutrient cycle of the water.
Water plants against algae in the pond help to reduce algae formation. The plants help to stabilise the biological balance in the garden pond and absorb many nutrients from the pond water. Underwater plants also produce oxygen and are in direct competition with algae. However, proliferating underwater plants can also quickly become a plague, e.g. in the case of water pollution. Nutrient-consuming aquatic plants such as bulrushes, calamus or reeds can also slow down or even completely stop the growth of algae.
Tipp: Nutrient absorbing Water plants list (PDF)
Which algae are particularly annoying?
Most owners of ponds and pools are particularly concerned about the stubborn thread algae. If they multiply particularly strongly, this is usually accompanied by a visible turbidity of the water. If the algae are not combated in time, pond owners in particular are at particular risk. At some point the algae die and sink to the bottom of the pond. As a result, the algae decompose over time, which can reduce the oxygen concentration. In the worst case, the concentration drops so low that the fish literally suffocate. This is called "tipping over" the water. In general, you should therefore always pay attention to early control of the algae. Dead algae and algae residues should be removed from the water regularly, this applies to both pond and pool owners.
Fight green algae in the pond

What to do when green algae cover the pond?
Green algae spread out with a surplus of nutrients, plenty of sun and shallow water. To prevent green algae from spreading excessively, the pond must be thoroughly cleaned. The nutrients are removed from the pond manually with a landing net and bucket or with a sludge vacuum cleaner.
The first rule to be recommended: after cleaning the pond, only top up with low-nutrient tap water or rainwater and strongly growing nutrient-consuming water plants. Shading the pond, natural helpers such as starter bacteria, water fleas, daphnia and brook flea crabs also help.
As a first aid for green algae in the garden pond, if no success is visible after several weeks, there is the natural algae destroyer. Further information summarised in our conclusion on algae control.
Fight floating algae in the pond

Cloudy, green pond water is an indication of floating algae, which spread rapidly in the pond when there is a lot of sun and heat.
Floating algae in the pond is quickly detected by green pond water. Suspended algae are mainly formed in ponds with an excess of nutrients, e.g. Koi ponds, ponds with birds. Often a filter system or sufficiently large plants are missing to extract the nutrients from the water.
Immediate measures against floating algae
Algae remedies on a chemical basis only help for a short period of time for a few weeks. For a long-term immediate measure against floating algae a G-Sonic Algae destroyer helps to quickly kill the floating algae. As a further measure against the cloudy pond water, pond plants should be planted against the formation of floating algae. Pond plants are the biggest food competitor for algae in the pond and help to make the green pond water clearer. Filter systems with UV light against floating algae are praised as a very effective method. However, it is a fact that the use of a UVC pond clarifier kills many vital micro-organisms and only a not too strong UV lamp should be used.
How can I fight thread algae?
Threaded algae are long-threaded green algae. The thread algae pull fine green threads with them and like to have currents. Like floating carpets or tufts, thread algae form and when you look at them they look soft and loose. More informationen on thread algae.
Blue-green algae - how toxic are the blue-green algae, genus Tychonema / Microcystis or Cynanobacteria called?

Blue-green algae on the pond water water are toxic to humans and animals - algae bloom carpet (above), dead algae (below).
Blue-green algae have no cell nucleus and are bacteria living in water. The scientific name is therefore Cyanobacteria, Cyanobacteria or also Blue Green Algae. Blue-green algae live photosynthetically on naturally occurring waters. Algae blooms can form on the water, an oily film on the water surface is often seen. This oily film leads to health problems for humans and animals, as cyanobacteria can form toxic compounds (poisons). The best known blue-green algae species is the microcystins of the genus Microcystis. The toxic Tychonema blue-green algae is also widespread. Cyanobacteria in the so-called algal blooms can lead to poisoning when fish or mussels are consumed due to the toxins they contain. Many lakes turn green in summer and the algae spoil the fun of swimming, as bathing is prohibited because of the harmful blue-green algae. Blue-green algae are spreading to more and more inland waters due to the rise in temperature and hot summer days. The consequences of blue-green algae cause skin irritation and, if swallowed, lead to dizziness and vomiting. The nervous system and the liver are attacked and are especially dangerous for children. Wild animals, foxes, wild boars and dogs are particularly at risk and can die after drinking the infested water in the edge of the lakes. More informationen on blue-green algae and how to fight them.
Brown algae in the pond are mostly gravel algae

Brown algae lat. Phaeophyceae are widely distributed in the sea. In garden ponds they form a large group of brown algae of different appearance.
Algae that look brownish are often called brown algae. These can be diatoms lat. Bacillariophyta or brownish looking algae. Especially in hard water, silicic acid is present and is a vital factor for the diatoms. Often the silicic acid is introduced into the pond by the tap water.
In salt water there are about 1850 species of brown algae. Among the most famous brown algae are: Winged kelp (Alaria esculenta), knotted kelp (Ascophyllum nodosum), forked kelp (Bifurcaria bifurcata), spiked kelp (Desmarestia aculeata), sawdust kelp (Fucus serratus), spiral kelp (Fucus spiralis), finger kelp (Laminaria digitata), sugar kelp (Saccharina latissima)
Five species are known in fresh water. For pond owners, brown algae can become a real nuisance. The brown algae spread quickly and uncontrolled and take away light and nutrients from the plants.
Conclusion
In summary, algae in the pond, garden pond, swimming pond, natural pool, etc. can be successfully controlled by cleaning the pond, controlling the water quality and its water values, so that not too many nutrients are introduced. Aquatic plants such as rushes, bulrushes, reeds, sedges, marsh irises, perennials should be present in sufficient quantities to remove nutrients from the water.
Natural algae control is achieved by using a G-Sonic Algae remover. The devices fight all types of algae in freshwater effectively and in the long term. How does it work? By means of high-precision clicks, inaudible for humans and animals, which are sent under water through the pond. An effective and simple way to fight algae!


